
SOCIOLOGY UPSC – PAPER 1 – Sociological Thinkers : Max Weber- Social action, ideal types, authority, bureaucracy, protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism.
- Weber was one of the pioneers of discipline of sociology.
- He mainly used Interpretivist approach.
- Father of modern sociological thought.
- Advocated to focus on micro level on the individual.
- He bridged the gap between positivism and idealism.
- Favoured the use of scientific method.
- Developed the scope of sociology as the meanings attached by the actors to their actions.
SOCIAL ACTION
- Weber used Social Action and Ideal Types as the basis of his theoretical framework.
- Subject matter of Sociology is to study Social Action.
- Social Action – Any action is social by the virtue of the meaning attached to it by the actors, it takes into account the behaviour of others and is thereby, oriented in its course.
- Conditions for an action to become a social action:
• Action is social if some meaning is attached to it by the actor. Actor must be conscious of his or her action. The meanings are in the form of motivation of an individual.
• Action is social if it is oriented to some other, i.e, only those actions are social which are taken in orientation to some other object.
• Excluded imitative actions and mass conditioned actions
VERSTEHEN
- Literally means comprehending or understanding at the level of the actor.
- It is one of the tools for interpretative understanding.
- It involves the comprehension of the meaning by using simple steps of investigation:
• Investigator should reconstruct the situational choices and constraints of the actor.
• Investigator should be at the same wavelength as that of the actor.
• Investigator should not have any sympathy with the actor of the situation.
• Investigator can use primary sources of data collection to establish meanings.
IDEAL TYPE
- Verstehen cannot be used alone and should be used with other methods like ideal type.
- Ideal type is a mental construct which is used to identify certain regularities in social life.
- Used to further understand the meanings attached by the actors.
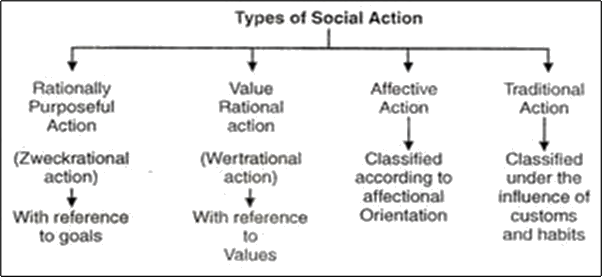
Four Ideal types
- Traditional Social Action
Meanings are drawn from certain beliefs and traditions.
Involves least conscious thinking over action. - Affective Social Action
Meanings are generated due to emotions of an actor.
Like love, hatred, anger, etc. - Zweckrational Social Action
These actions are end or goal-rational actions.
Actions are more logical and ends are logically defined.
It is the most conscious action. - Wertrational Social Action
It is called value oriented rational actions.
The goal is defined by the values of the society and the actor takes logical action inorder to fulfill that goal.
Significance - Any actual action can be compared with this ideal types of actions and meanings can be attached.
- Ideal type methodology provides investigator with readymade models and saves time of the investigator.
CRITICISM
- Greater stress on individual meanings and ignores influence of social structure in the understanding of reality.
- His claim of objectivity is also not true. Ideal types are highly susceptible to subjectivity of the investigator.
- Collective action is ignored.
- Weber also ignore some unintended meanings and consequences of social action.
- Parsons expanded the meaning of social action by including situational choices, constraints and aspiration of the actor as well.

